STORY
A story is
basically a narrating of
real or imaginary events,
involving real or imaginary people. A short story is a short
work of fiction. Fiction, as you know, is prose writing about imagined events
and characters. Prose writing differs from poetry in that it does not depend on
verses, meters or rhymes for its organization and presentation. A story is generally designed to entertain, and/or send a message
across.
The length of a written story will depend on the
format, whether it is a novel, novella, short story etc. The length of a story
has no bearing to its quality.
Structure/Format of a Story
There is a basic
structure one can follow. It helps construct a story in an understandable
manner and keeps the flow of the story.
Beginning: The beginning or the introduction of a story is of essential importance.
This is the part where you can hook the reader and capture their attention. You
must have come across some often-used beginnings to stories like, “Once upon a
time” or “A long time ago”. However, you can get more creative and begin your
story with intrigue.
Character Introduction: Your story will depend heavily on how well
you introduce your characters. To
develop your characters, you can use dialogues as well. Also, do not include
unnecessary secondary characters. Every character of the story must have a
purpose.
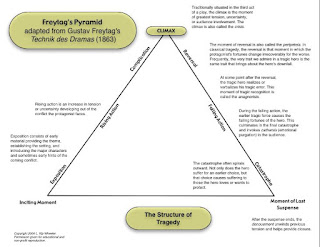
Plot: A plot is a
series of events and character actions that relate to the central conflict.Here is where the actual narration of the story will happen. The events that occur or the description
of the situation will be written in the plot. A plot must always have a
conflict, which is the focus of any story.
Plot and Structure
The plot is the main sequence of events that make up the story. In short stories the plot is usually centered around one experience or significant moment. Consider the following questions:
- What is the most important event?
- How is the plot structured? Is it linear, chronological or does it move around?
- Is the plot believable?
Climax/Conclusion: And
this is where the story will come to its logical conclusion. If there is a plot
twist, this is where you will include it. Always end your story in an
interesting manner. Also, it is not necessary to give your story a definite
ending.
American literature contains some of the world's
best examples of the short story. Readers around the world enjoy the finely
crafted stories of American writers such as O. Henry, Stephen Crane, Jack
London, Mark Twain and Edgar Allen Poe.
What makes these authors such remarkable short
story writers? They are true masters at combining the five key elements that go
into every great short story: character, setting, conflict, plot and theme.
A character is a person, or sometimes even an animal, who
takes part in the action of a short story or other literary work.
Characterization
Characterization deals with how the characters in the story are described. In short stories there are usually fewer characters compared to a novel. They usually focus on one central character or protagonist. Ask yourself the following:
- Who is the main character?
- Who or what is the antagonist?
- Are the main character and other characters described through dialogue – by the way they speak (dialect or slang for instance)?
- Has the author described the characters by physical appearance, thoughts and feelings, and interaction (the way they act towards others)?
- Are they static characters who do not change?
- Are they dynamic characters who change?
- What type of characters are they? What qualities stand out? Are they stereotypes?
- Are the characters believable?
- Do the characters symbolize something?
Setting
Setting is a description of where and when the story takes place. . Authors often use descriptions of landscape, scenery, buildings, seasons or weather to provide a strong sense of setting.In a short story there are fewer settings compared to a novel. The time is more limited. Ask yourself the following questions:
- How is the setting created? Consider geography, weather, time of day, social conditions, etc.
- What role does setting play in the story? Is it an important part of the plot or theme? Or is it just a backdrop against which the action takes place?
- Does the setting change? If so, how?
Study the time period, which is also part of the setting, and ask yourself the following:
- When was the story written?
- Does it take place in the present, the past, or the future?
- How does the time period affect the language, atmosphere or social circumstances of the short stor
CONFLICT: Conflict or tension is usually the heart of the short story and is related to the main character. In a short story there is usually one main struggle.The conflict is a struggle between two people or things in a short story. The main character is usually on one side of the central conflict.
On the other side, the main character may struggle against another important character, against the forces of nature, against society, or even against something inside himself or herself (feelings, emotions, illness).
- How would you describe the main conflict?
- Is it an internal conflict within the character?
- Is it an external conflict caused by the surroundings or environment the main character finds himself/herself in?
CLIMAX: The climax is the point of greatest tension or intensity in the short story. It can also be the point where events take a major turn as the story races towards its conclusion.
RESOLUTION: The resolution is the end of the story. It focuses on how the conflict is ultimately resolved.
- Are the closing sentences significant? How does the end relate or connect to the opening?
Narrator and Point of View
The narrator is the person telling the story. Consider this question: Are the narrator and the main character the same?
By point of view we mean from whose eyes the story is being told. Short stories tend to be told through one character’s point of view. The following are important questions to consider:
- Who is the narrator or speaker in the story?
- Does the author speak through the main character?
- Is the story written in the first person “I” point of view?
- Is the story written in a detached third person “he/she” point of view?
- Is there an “all-knowing” third person who can reveal what all the characters are thinking and doing at all times and in all places?
- Is the narrator trustworthy?
Theme
The theme is built on a topic, such as death, hope, the American dream, etc. and how the topic affects the human condition, society, or life. As a reader, focus on what the story is revealing about the topic. The theme should be expressed as a statement, a general observation about human nature.The theme is the central idea or belief in a short story.
What a theme is NOT:
- a word or phrase (topic or subject)
- a command
- a judgment
To help you construct the thematic statement, make a list of important images, topics, etc. found in the text. Try to create a statement that includes the words in your list.
NOVELS
Novels are another example of fictional prose and
are much longer than short stories.
NOVELLA
Some short stories, however, can be quite long. If
a a short story is a long one, say fifty to one hundred pages, we call it a
novella.



No comments:
Post a Comment